Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation is usually is easy to avoid and easy to treat when it occurs. Occasionally, symptoms of constipation may be a sign of a more serious problem requiring medical attention.
This educational piece is intended to address:
-
The basics of good intestinal health and function and how to avoid constipation
-
What constipation is and what might be at its cause
-
Review how to evaluate constipation and how a colon and rectal specialist may be of help
-
The medical treatment of constipation – conservative measures, role of laxative therapy, and possible benefits of other medications
-
The limited role of surgery for the treatment of constipation and the specific indications for when it might be the best available treatment
WHAT IS NORMAL BOWEL FUNCTION?
After eating, food is transported through the small intestine, where it is broken down and the nutrients are absorbed. The remaining liquid waste then passes into the colon. The colon removes water and certain electrolytes, turning the liquid waste into a more solid form. It then passes into the rectum, where it is stored until it is time to have a bowel movement. Discussion of bowel function can be broken down into four main components:
- Frequency- how often you move your bowels
- Ease of evacuation of stool- is there a need to strain
- Firmness of stool- how hard is the stool
- Sense of complete evacuation of stool- do you feel stool is stuck in the rectum
There is a wide range of what are considered “normal” bowel habits. In general, bowel movements should occur at least every 1-3 days and no more than three times per day. Stool should pass easily and not require excessive straining. Lastly, one should experience a sense of completeness of elimination. The belief that one must have a bowel movement every day simply is not accurate and can lead to unnecessary concern and even abuse of laxatives. In fact, if one’s daily bowel movement is hard, requires great effort to expel, or does not satisfactorily empty, the individual would still be considered to have constipation in spite of having a “normal” frequency. On the contrary, if one has a bowel movement every third day but it is not hard, does not require straining, and completely evacuates, then one may very well consider this a “normal” bowel movement.
Bowel movements require that the colon moves stool towards the rectum in a coordinated and predictable fashion. Bulkier stool better stimulates contraction of the muscles within the wall of the colon. High fiber diets produce larger, bulkier stool and improves bowel movements. As the stool passes into the rectum, one experiences stretching of the rectal wall which creates the sensation of the need to evacuate. If a person is not in an appropriate place to have a bowel movement, contraction of the sphincter muscles stops evacuation and the sensation to go ceases. When in the appropriate place (such as a bathroom), squatting and abdominal pressure initiates evacuation of the stool from the rectum. It is important to understand that coordinated reflex relaxation of pelvic and sphincter muscles is required to allow elimination. Certain muscles need to contract while others need to relax at the same time in order for the stool to pass easily. The stretch sensation caused by the stool in the rectum should then be relieved with a sense of complete evacuation.
DEFINING CONSTIPATION
Given the four main components of bowel function described above, constipation may mean different things to different persons. For some, constipation may mean infrequent bowel movements. To others, it is a hard stool which may be difficult to pass and requires excessive straining. Lastly, constipation may mean a bowel movement which does not completely evacuate and leaves the person with a sense that they still “need to go.” Some patients have combinations of these symptoms. As one can see based on the various combinations of symptoms, it can be somewhat difficult to specifically define what constipation is.
In an effort to better define constipation, specific criteria were established by the ROME Multinational Consensus in 2000, and subsequently updated last in 2016:
- Less than three bowel movements per week
- Straining more than 25% of the time
- Hard stools more than 25% of the time
- Incomplete evacuation or sense of blockage more than 25% of the time
- Need to use your hand to pass the bowel movement at least 25% of the time
The purpose of these criteria was to develop a more specific definition, to enhance research, and to help evaluate treatment outcomes.
It is important to keep in mind that constipation must be differentiated from irritable bowel syndrome, constipation subtype (IBS-C) which is associated with abdominal pain, irregular bowel habits (intermittent loose stools not associated with laxatives), and pain relieved by defecation. One can find more information regarding irritable bowel syndrome at www.fascrs.org.
WHAT CAUSES CONSTIPATION?
Causes of constipation include:
-
Lack of dietary fiber
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Dehydration
-
Medical conditions – e.g., hypothyroidism, diabetes, scleroderma, lupus, depression
-
Medications – e.g., narcotic pain medications, blood pressure medications, and psychiatric medications
-
Abnormal function – colonic inertia, pelvic floor muscle dyssynergia, Hirschsprung’s disease
-
Colon or rectal cancer
-
Anal cancer
-
Anatomic reasons - enterocele, sigmoidocele, rectocele, and rectal intussusception, or prolapse
-
Colonic stricture or narrowing caused by diverticulitis, Crohn’s disease, radiation induced, and ischemia
Constipation is common and probably represents the most common intestinal complaint. Constipation is often due to a combination of three factors: low fiber diet, poor fluid intake, and lack of physical activity or exercise. All of these are important to intestinal health and normal function, and simply addressing them will often improve bowel movements and relieve constipation. At times, other causes must be considered. Specific medical conditions can cause constipation, including diabetes, low thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism), and depression, or other less common diseases such as scleroderma, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis. Medications may contribute to constipation, including those commonly prescribed for pain relief, high blood pressure, antidepressants, psychiatric drugs, and antacids. It is critical to know what medications you are currently taking and discuss their possible side effects with your medical provider or pharmacist.
Some specific types of constipation are rare, but occasionally must be taken into consideration when chronic constipation remains unresponsive to simple measures. These include slow transit constipation (motility disorder where the colon does not move stool through as it should), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and dyssynergic defecation (the rectum does not evacuate stool the way it should), or a combination of the above (mixed disorder). Lastly, some serious causes of constipation are more mechanical in nature. Diseases which cause inflammation like diverticulitis or Crohn’s disease can cause excessive scarring and narrowing. In addition, tumors or growths in the colon can physically block the bowel. These less common causes should be kept in mind, as they are often more serious.
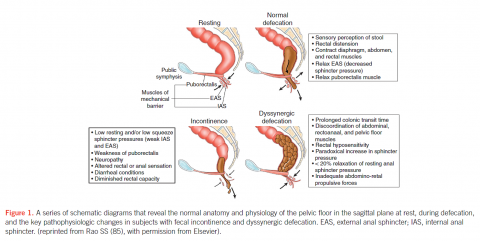

Figure 1 R. Schey, J. Cromwell, and S. Rao Am J Gastroenterol 2012; 107:1624–1633; doi:0.1038/ajg.2012.247; published online 21 August 2012
HOW DO YOU TREAT CONSTIPATION?
Generally, constipation is avoided by following the basics of good intestinal health. Diet, fluid intake, and physical activity should always represent the initial steps when an individual experiences constipation. Twenty-five to thirty-five grams of fiber per day is the recommended daily amount of dietary fiber. Eating a diet rich in whole grain breads, cereals and fiber bars, in addition to fresh fruits and vegetables, often will improve bowel habits by adding bulk to the stool. Fiber and fiber supplements, however, are not an antidote for poor dietary habits, such as eating fried or fatty foods and frequent red meat. Healthy dietary choices are the foundation of intestinal health and bowel function. What foods are taken into the body affect how waste is eliminated.
Scientific studies have shown that drinking 6 to 8 glasses of water per day (1.5-2 liters) will help keep the stool from being hard and makes it easier to eliminate. Regular exercise, which can be as simple as taking a brisk walk for 30 minutes per day, will likely improve bowel movements as well.
ROLE OF LAXATIVES
There are many different types of over-the-counter laxatives available. The way in which laxatives work varies and can be very effective for acute relief of constipation and, in rare cases, may be part of a regular routine. Before one resorts to routine laxative use, it is important to discuss your symptoms with your medical provider, as a more serious medical condition may need to be ruled out.
Irritant-type laxatives (cathartics) stimulate bowel wall contraction. Examples of this class of laxatives include senna, cascara sagrada, or bisacodyl-based medications. The long term use of such stimulant laxatives may result in tolerance and over time, bowel function may become ineffective. Chronic use is generally discouraged. Another class of laxatives are the osmotic-type laxatives which promote water retention in the bowel. These laxatives may be based on salts or sugars as the active molecules creating the osmotic effect (pulling water into the colon). Sugars such as lactulose or sucrose are available. Magnesium-based (Milk of Magnesia®, magnesium supplements) products can also act as osmotic laxatives, although care must be exercised in patients with kidney problems, as such types of laxatives may cause electrolyte problems in patients with kidney disease. Polyethylene glycol 3350 (MiraLAX®) is an over-the-counter osmotic laxative which increases bowel frequency and is commonly recommended as a result of its safety. Other laxatives improve passage of stool by affecting the character of the fecal material. Mineral oil prevents fluid loss by coating the stool. Docusate sodium (Colace®) enhances water penetration into the stool, making it softer and is not a true laxative.
Enemas and suppositories also have been used to treat constipation. Enema and suppository therapy stimulate defecation through distension of the rectum (saline) or by irritation (soap suds, Fleets®, bisacodyl) or by softening the stool (glycerin suppository). Unfortunately, a downside of such a strategy is that it can be habit forming, and tolerance to such stimulation may diminish effectiveness long term.
Again, it must be stressed that while laxatives, enemas, and suppositories may all play a role in the treatment of constipation, their chronic use should be discouraged without first consulting with your medical provider to ensure that a more serious condition is not overlooked.
SPECIFIC MEDICATIONS TO TREAT CONSTIPATION
Specific medical therapies exist to treat constipation. These therapies are prescribed by your medical provider only in certain circumstances, and cost may be an issue. One available medication is lubiprostone (Amitiza®). This medication works by increasing intestinal secretion. While this medication is safe, the side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and headaches, which may limit its effectiveness. Linaclotide (Linzess®) is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a medical therapy for constipation. This drug works by increasing both motility and by increasing intestinal secretion. Another medication approved in Europe and Canada for the treatment of constipation in females, prucalopride (Resolor®, Resotran®), works by increasing bowel motility. Unfortunately, the number of males studied was insufficient to demonstrate benefit in this group. Currently, prucalopride has not yet been approved for use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration but offers a possible future treatment option. Another medication which treats constipation specific to individuals taking chronic narcotic pain medications due to chronic pain resulting from advanced illness is methylnaltrexone bromide (Relistor®) and Naloxegol (Movantik®). These have been approved for opioid-induced constipation (OIC) and works by counteracting the negative effects of narcotic pain medications on bowel motility. This again requires medical evaluation and a prescription. Cost will be an issue for those whose medication benefit plan does not cover this relatively new drug.
ASSOCIATED SYMPTOMS AND WHEN TO SEEK HELP FROM YOUR MEDICAL PROVIDER OR A SPECIALIST
Knowing when constipation requires professional evaluation is key. In general, if constipation becomes progressive either in frequency or severity and not manageable with the simple measures described above, one should seek medical attention. Constipation often is accompanied by other symptoms which can be very important in terms of determining the nature of the problem and knowing when you should see a medical provider. Not infrequently, constipation is associated with a bloating sensation, mild nausea, and perhaps mild cramping pain, all of which are generally relieved by bowel movements. Clearly, if one has worsening nausea and repeated vomiting or if abdominal pain becomes severe and constant, one should seek immediate help. Also, if constipation is associated with a change in stool size — narrow like a pencil or ribbon — change in stool frequency, or if any blood is seen, one should see a medical provider.
HOW DO YOU EVALUATE CONSTIPATION?
There are several tests that could be considered when constipation persists in spite of basic measures or if the constipation is associated with other symptoms.
Considering the normal function of the colon and rectum, constipation can be understood as failure of the colon to adequately push the stool forward, failure to sense distension or fullness of the rectum, or failure of the coordinated reflex relaxation of the pelvic muscles to allow for evacuation of stool. Rare anatomic abnormalities (rectocele, enterocele, sigmoidocele) can inhibit normal evacuation. Constipation can be a result of mechanical blockage of the bowel by scarring and constriction of the bowel lumen or by narrowing of the lumen due to growth of a tumor or mass.
Diagnostic studies to evaluate constipation include:
- Colonoscopy
- Barium enema
- CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy)
- Colonic transit study (Sitzmarks® study)
- Anorectal manometry
- Defecography – fluoroscopic (traditional) or dynamic MRI
Colonoscopy is a test where a lighted flexible tube with a video camera at its tip is passed through the anus, rectum, and colon, allowing for visualization of the lumen of the bowel and inspection for growths such as polyps or masses. Colorectal cancer is common in the U.S. and should always be high on the list for possible causes of blockage of the colon and a potential cause of constipation. Colonoscopy has the advantage of patient sedation and is generally better tolerated as a result. Colonoscopy should not be performed when acute diverticulitis is suspected due to the risk of perforation. Colonoscopy has a very small risk (about 1 in 1,000) of perforating the colon or causing bleeding severe enough to require a blood transfusion and/or surgery. It is the most sensitive test, however, for detecting polyps (precancerous growths), allows for removal of such polyps, and allows for biopsy of any other lesions detected.
Barium enema is an x-ray test involving passage of an enema containing contrast into the rectum and colon with subsequent multiple abdominal x-rays performed, providing information related to the bowel lumen and the presence of masses or narrowing of the lumen. It is less commonly performed than colonoscopy, but may be complementary to colonoscopy when evaluating narrowing of the bowel due to scarring. Disadvantages of a barium enema are that it again requires bowel cleansing, is performed in the awake patient, is not as sensitive at detecting polyps, and, if abnormal, requires subsequent colonoscopy to be performed for further evaluation.
A special CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis (CT colonography) or “virtual colonoscopy” may also be considered as an alternative radiology study, but just as in the case of an abnormal barium enema, a colonoscopy would then be necessary if abnormalities were found. So, while there are options, diagnostic colonoscopy generally is considered the initial test of choice in a person with symptoms of constipation.
Rarely, severe constipation occurs due to lack of colonic muscular activity and failure to push stool to the rectum. This condition, known as colonic inertia, results in profound constipation where patients often may fail to have a bowel movement for weeks. Such constipation often develops in childhood, although not always. This may represent as few as ten percent of all patients presenting to medical attention for the evaluation of constipation. The cause of colonic inertia is unknown. Evaluation involves colonoscopy or barium enema to assess for mechanical blockage.
 Figure 2
Figure 2
If no blockage is found, the colon’s ability to propel stool can be determined by a colonic transit study where a patient swallows a capsule (Sitzmarks ®) with small rings (Figure 2) which can be seen on x-ray and followed by serial x-rays to assess the progress of the rings passing through the intestinal tract. In the simplified method, one capsule is ingested on Sunday and x-rays of the abdomen are performed on Monday, Wednesday and Friday. Usually, all the rings are expelled by the fifth day. An abnormal study is identified by 6 of 24 rings (>20%) remaining within the intestinal tract and there are two particular patterns which may be present. If more than 20% (6 or more) of the markers remain and are distributed throughout the colon, the study suggests colonic inertia or poor muscular activity of the colon and the failure of the colon to propel the stool (Figure 3).
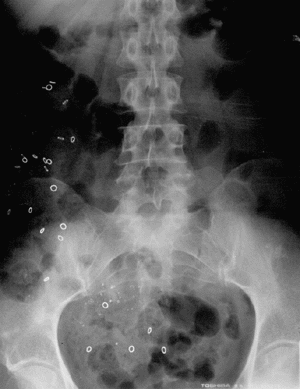
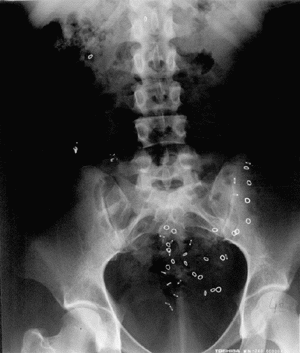
Figures 3 and 4
If more than 20% of the markers remain, but are pushed to the rectum and not expelled, this would suggest normal muscular activity of the colon, but indicate that there is a problem with the muscles of the pelvic floor (Figure 4). This would be referred to as dyssynergic defecation or pelvic outlet dysfunction syndrome (ODS). The pelvic floor muscles may fail to relax in a coordinated fashion (i.e pelvic floor dysfunction, pelvic dyssynergia, non-relaxing puborectalis muscle) to allow for evacuation. There may be an anatomic abnormality which inhibits or blocks normal evacuation such as an enterocele, sigmoidocele, rectocele, or rectal prolapse.
Pelvic floor function can be assessed on physical exam by assessing the ability of the anal sphincter and pelvic floor muscles to squeeze and relax normally. To confirm possible disorders of the anal sphincter muscles or pelvic floor function, a study called “anal manometry” can be performed to measure the pressures of the muscles at rest and when functioning. Anal manometry should be considered to evaluate for outlet obstruction when a patient feels that the rectum is distended and the desire to eliminate is present, but upon attempts to evacuate, the patient fails to do so. This suggests possible pelvic or anal outlet obstruction as the cause of constipation.
Manometry is done by inserting a thin tube into the anal canal and rectum and measuring pressures with various maneuvers. The test measures pressures at rest, upon voluntary squeeze, and with attempt to evacuate. In addition, a small balloon on the tip of the catheter can be inflated to assess sensation of rectal filling. Again, normal bowel function requires the ability to sense when the rectum is filling and stretching out. Balloon inflation also tests an important reflex of the anal sphincter muscles. Typically, during rectal filling and distension – simulated by the inflation of the balloon – we normally expect that measured pressures will briefly decrease in the anal canal. This reflex is known as the recto-anal inhibitory reflex and absence of this reflex may indicate failure of relaxation of the sphincter muscles to allow for evacuation. Both Chagas’ disease (caused by a parasite, usually found in Brazil) and Hirschsprung’s disease (a developmental absence of nerve endings in the anal sphincter muscle) result in failure of the anal sphincter muscles to relax and, thus, not allow for normal passage of stool out of the rectum.
Additionally, anal manometry may identify contraction instead of relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles during an attempt to evacuate, which may represent loss of the normal coordinated reflex. This failure of relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles again results in an inability to eliminate stool. During anal manometry, a balloon expulsion test can be performed. The catheter balloon is filled to 60 milliliters and the patient is instructed to evacuate the balloon. If the patient is unable to eliminate the balloon within one minute, the test is abnormal and suggests an anal or pelvic floor outlet dysfunction as the cause for constipation.
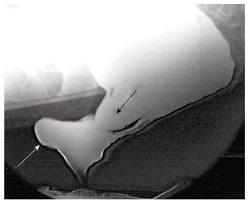 Figure 5
Figure 5
Defecography is an additional x-ray test utilized to evaluate the patient’s ability to eliminate stool properly. This involves drinking barium by mouth to fill the small intestine and inserting an enema of thick barium or paste (about the consistency of oatmeal) into the rectum. The patient then sits on a special commode and fluoroscopy (dynamic x-rays) is performed during a patient’s attempt to evacuate the paste from the rectum. This enables evaluation of the coordinated movement of the rectum and pelvic floor muscles to allow for evacuation of the rectum as well as to evaluate for possible anatomic abnormalities which may inhibit or block elimination. A variant of this test is a dynamic MRI.
In addition to identifying cases where the pelvic floor muscles do not relax normally during evacuation (pelvic dyssynergia), other anatomic abnormalities may also be discovered. An enterocele is a type of hernia at the pelvic floor where the small intestine pushes between the vagina and the rectum, thereby occluding the rectum during defecation. Similarly, a sigmoidocele occurs when the sigmoid colon descends into a pelvic floor defect and obstructs the rectum. Intussusception of the rectum or rectal prolapse can also cause occlusion by internally blocking the rectum. A rectocele is an outpouching of the rectum into the posterior wall of the vagina which will “pocket stool” and prevent normal passage of stool downward and out. These abnormalities are visualized by defecography. Identification of such abnormalities leads to careful selection of patients who may benefit from surgical repair and correction.
TREAMENT OF SEVERE CONSTIPATION AND SPECIFIC DISORDERS
In the case of pelvic floor non-relaxation (pelvic floor muscle dyssynergia), physical therapists can help patients retrain using special techniques (biofeedback) to improve sensation of rectal fullness as well as pelvic muscle relaxation to allow for elimination. The objectives of biofeedback are two-fold: To correct the dyssynergia or incoordination of the abdominal, rectal, puborectalis and anal sphincter muscles in order to achieve a normal and complete evacuation and, secondly, enhance rectal sensory perception (rectal filling or distension) in patients with impaired rectal sensation. The regimens for therapy vary, but a training session typically takes one hour. Patients usually undergo therapy everyone to two weeks and on average, four to six training sessions are required. Subsequent reinforcements at six weeks, three months, six months and twelve months may provide additional benefit and also improve the long-term outcome for these patients, but its efficacy has not been validated.
The results of biofeedback range depending upon the measured endpoints. Several randomized controlled trials of adults with dyssynergic defecation have been reported. While the studies differ in respect to their methods, all of these studies have concluded that biofeedback therapy is superior to controlled treatment approaches such as diet, exercise, laxative use, and other therapies. Identifying patients with dyssynergic defecation likely can lead to relief of constipation with biofeedback. Unfortunately, such therapy appears limited by the presence in medical communities of trained physical therapists dedicated to pelvic floor disorders.
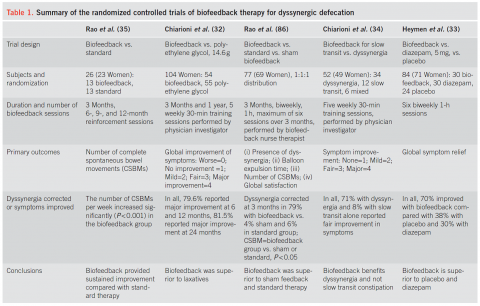
R. Schey, J. Cromwell, and S. Rao Am J Gastroenterol 2012; 107:1624–1633; doi: 10.1038/ajg.2012.247; 21 August 2012
Constipation is a problem rarely treated with surgery, but removing the colon for slow transit constipation may be considered. Patients considered for surgical correction of constipation should be thoroughly evaluated to ensure no evidence of dyssynergic defecation and verify normal stomach emptying and small intestinal transit by a physician and undergo appropriate testing. These patients should also have failed maximal medical management.
Colonic inertia or slow transit constipation refers to a lack of normal movement of stool through the colon and results in infrequent bowel movements. The operative procedure to treat slow transit constipation involves removal of the colon (total abdominal colectomy - TAC) with either reconnection of the small intestine to the rectum (ileorectal anastomosis- IRA) or, alternatively, creation of an end ileostomy (intestine brought out through the abdominal wall and skin to empty into a bag). The procedure often can be performed using a laparoscopic technique involving camera-guided surgery, small instruments, small incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and quicker return to regular activities. After TAC with IRA, the patient should expect to have multiple (3-5) loose stools per day. Although constipation is reliably relieved by TAC with IRA, significant issues remain regarding a patient’s sense of the quality of life and satisfaction associated with this treatment.
TAC with IRA can be associated with abdominal pain, diarrhea, incontinence, and recurrence of constipation. Patients should be counseled that the abdominal pain and bloating may persist postoperatively even after normalization of bowel frequency. A specific group of patients vulnerable to poor outcomes following TAC with IRA are patients who suffered prior sexual abuse. These patients, in particular, require more post-colectomy medical care for abdominal complaints. Thus, prior to surgery for colonic inertia, patients should be extensively counseled about the risk of persistence of symptoms and the potential for development of new symptoms after surgery.
As previously discussed, pelvic floor hernias and rectocele of the rectum can be repaired when identified on defecography. Lastly, specific diseases which have narrowed the bowel due to inflammation (diverticulitis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, ischemic colitis) or due to colorectal cancer will require surgery.
It is very important to emphasize that the role of surgery in the treatment of constipation is for very specific diseases or disorders. The reality is that patients with constipation will rarely require an operation. Referral to a colon and rectal surgeon should be viewed as an opportunity to have an expert evaluate a patient in the most efficient and logical manner, hopefully resulting in an effective and rational treatment of constipation.
SUMMARY
Constipation is a common complaint which is most often avoided or addressed by thoughtful dietary choices to increase fiber and fluid intake and by lifestyle changes to include regular exercise. If these measures fail to improve your bowel habits, talk to your doctor or medical provider to be evaluated. Laxatives should not be regularly taken without first talking to your medical provider. Lastly, if constipation is associated with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, acute abdominal pain, or blood from the rectum, one should immediately seek medical attention to evaluate the cause of the complaints. Medical management is usually effective in relieving symptoms, while surgery is reserved for very specific situations and gives good results in the right patient.
QUESTIONS FOR YOUR MEDICAL PROVIDER:
- Do you have recommendations or information on high fiber diet?
- Are any of my medical conditions causing my constipation? Are side effects of my medications contributing to my constipation?
- When should I get a colonoscopy? Do I need additional tests other than a colonoscopy?
- Should I see a colon and rectal surgeon for evaluation of constipation?
WHAT IS A COLON AND RECTAL SURGEON?
Colon and rectal surgeons are experts in the surgical and non-surgical treatment of diseases of the colon, rectum and anus. They have completed advanced surgical training in the treatment of these diseases as well as full general surgical training. They are well-versed in the treatment of both benign and malignant diseases of the colon, rectum, and anus and are able to perform routine screening examinations and surgically treat conditions if indicated to do so.
DISCLAIMER
The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons is dedicated to ensuring high-quality patient care by advancing the science, prevention and management of disorders and diseases of the colon, rectum and anus. These brochures are inclusive but not prescriptive. Their purpose is to provide information on diseases and processes, rather than dictate a specific form of treatment. They are intended for the use of all practitioners, health care workers and patients who desire information about the management of the conditions addressed. It should be recognized that these brochures should not be deemed inclusive of all proper methods of care or exclusive of methods of care reasonably directed to obtain the same results. The ultimate judgment regarding the propriety of any specific procedure must be made by the physician in light of all the circumstances presented by the individual patient.
CITATIONS
S. Rao & K. Meduri, “What’s Necessary to Diagnose Constipation,” Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 February ; 25(1): 127–140
M. G. Varma and B. H. Gurland. Chapter 32, “Constipation and Functional Bowel Disorders,” Chapter in Beck, D. E., Roberts, P.L., Saclarides, T.J., Senagore, A.J., Stamos, M.J., Wexner, S.D.,, Eds. ASCRS Textbook of Colon Rectal Surgery, 2nd Edition. Springer, New York, NY;2011
S. Rao, “Biofeedback Therapy for Constipation in Adults.” Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 February; 25(1): 159–166.
SUGGESTED READING:
C. A. Ternent, A. L. Bastawrous, N. A. Morin, et al and the Standards Practice Task Force of The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons., “Practice Parameters for the Evaluation and Management of Constipation.” Diseases of the Colon & Rectum 2007; December; 50(12):2013-19
Ford, A.C., Talley, N.J., “Laxatives for Chronic Constipation in Adults.” British Medical Journal 2012;Oct 1;345:e6168